You must visit the Child Dental Center (CDC) in your locality because these are
dental clinics run by dentist having specialized training for oral health issues
relating to children. Please understand that poor oral health can limit a child's
development and participation in life activities.
The Dentist at CDC will be able to Check the Oral Health Status of your Child Regarding
the Following:-
- Tooth decay
- White Spots
- Periodontal disease
- Dental whitening
- Abnormalities in developing dentition
- Oral habits
- Traumatic injuries
Tooth Decay
It is important to understand what is tooth decay, because it affects your child's
growth, results in significant pain and diminish overall quality of life.
Dental caries is a common chronic infectious transmissible disease resulting from
tooth- adherent specific bacteria, primarily mutans streptococci (MS) that metabolize
sugars to produce acid which, over time, demineralizes tooth structure.
How Children Get Cavities
- Tooth decay germs (microbes) pass (vertical transmission) from mother to child.
- By eating sugary, starchy, or sticky foods that feed the germs.
- Teeth not cleaned every day.
Germs + Carbohydrates = Acid
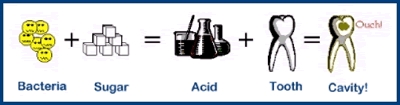
Dental caries results from an interaction between oral flora and dietary carbohydrates
on the tooth surface. Oral flora utilizes dietary sugars to create a sticky biofilm
that is referred to as dental plaque.Acids produced by bacterial fermentation of
carbohydrates reduce the pH of dental plaque to the point at which demineralization
of the enamel occurs.
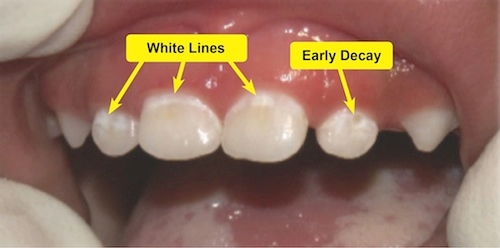
White Spots
The initial carious lesion appears as an opaque white spot on the enamel. These
white spots can quickly become dark (yellow-brown) cavities (within 30 days) if
not treated timely by a dentist.
Get your child's teeth checked once a month for white spots at CDC.
Oral Health Guidelines by CDC
All children should be taken to the Child Dental Centre (CDC) regularly for a full
clinical examination by a dentist. Dental caries is a disease that generally is
preventable.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease or gingivitis is characterized by the presence of gingival inflammation
without detectable loss of bone. Normal and abnormal fluctuation in hormone levels,
including changes in gonadotrophic hormone levels during the onset of puberty, increases
the gingival's response to plaque. Similarly, alterations in insulin levels in patients
with diabetes can affect gingival health.
Gingivitis is a reversible disease. Early diagnosis at Child Dental Center (CDC)
ensures successful treatment.
Dental Whitening
Discolored tooth or teeth seriously affects adolescents. Teeth can discolor due
to intake of drinks, beverages, fluorosis, traumatic pulpal changes, white spots
or tetracycline staining. The dentist at CDC will conduct an initial professional
examination to help identify causes of discoloration and treatment.
Abnormalities in Developing Dentition
Clinical examination by dentists at CDC will help in diagnosis of the following:-
- Missing,
- Supernumerary,
- Developmentally defective, and
- Fused or geminated teeth;
- Ectopic eruption; and
- Space and
- Tooth loss secondary to caries.
These abnormalities in the developing dentition cause malocclusion, dental crowding,
ectopic eruption, impaction, obstruction sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), oligodontia,
oral habits, posterior cross- bite and tooth size/arch length discrepancy.
Oral Habits
The habits of non-nutritive sucking, bruxing, tongue thrust swallow and abnormal
tongue position, self- injurious/self-mutilating behavior, and airway obstruction
(OSAS) apply forces to the teeth and dentoalveolar structures.
If the child continues habits with frequency, over a duration, and intensity --
results in deformation of dentoalveolar or skeleton. This can be open bite, protruded
teeth, increased over-jet, reduced overbite, posterior crossbite, or long facial
height.
Non-nutritive sucking is considered normal in infants or young
children. Visit CDC for guidance to help your child to stop by age 36 months or
younger.
Bruxism an occur while awake or asleep due to emotional stress,
para-somnias, traumatic brain injury, neurologic disabilities and (morphologic factors)
eg, malocclusion. This results in dental attrition, headaches, temporomandibular
dysfunction and soreness of the masticatory muscles. Dentists at CDC will educate
both the patient/parent, provide occlusal splints or psychological techniques or
medications as needed.
Tongue thrusting is associated with anterior open bite, abnormal
speech, seek advise and treatment from dentist at CDC.
Self-injurious or self-mutilating behavior (ie, repetitive acts
that result in physical damage to the individual) is extremely rare in the normal
child. Such behavior, however, has been associated with mental retardation, psychiatric
disorders, developmental disabilities, and some syndromes. Visit CDC for treatment
options for developmentally disabled individuals which can include pharmacologic
management, behavior modification, and physical restraint. Dentist may suggest lip-bumper
and occlusal bite appliances, protective padding, or extractions at CDC.
Malocclusion results in mouth breathing which increases facial
height, anterior open bite, increased overjet, and narrow palate.
Obstruction sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is linked to narrow maxilla,
cross-bite, low tongue position, vertical growth, and open bite. If your child snores,
has a restless sleep, day-time neurobehavioral abnormalities or sleepiness, or bed-wetting
visit CDC for advise regarding consequences of a habit.
Traumatic Injuries
Traumatic injures on the face (fractures, displaced, or lost teeth) have negative
functional, esthetic, and psychological effects on children. The maximum number
of traumatic injuries (primary teeth) occurs at 2 to 3 years of age, when motor
coordination is developing. Permanent teeth can suffer injuries due to falls, accidents,
violence or sports.
Physical Abuse
If you suspect that your child has suffered from physical abuse visit CDC. Intra-oral
and peri-oral examination by the dentist at CDC will certify craniofacial, head,
face or neck injuries. Signs of burns, or lacerations of the tongue, lips, buccal
mucosa, palate (soft and hard), gingiva, alveolar mucosa, or frenum; fractured,
displaced, or avulsed teeth; or facial bone and jaw fractures will signify to abuse.
Discolored teeth may be result from previous trauma. Gags applied to the mouth may
result in bruises, lichenification, or scarring at the corners of the mouth. Unintentional
or accidental injuries, injuries in different stages of healing will arouse a suspicion
of abuse.
Your child MUST visit CDC for Healthy Teeth for a Lifetime.